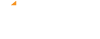2026 fund operations trends are taking a new shape, driven by pressure rather than ambition.
Private markets fund operations have expanded into a broad, complex industry. According to S&P Global, 2024 global private AUM approximated $15 trillion, and is expected to reach over $18 trillion by 2027.
At this scale, operational gaps do not stay hidden for long.
For GPs, fundraising becomes selective, LP scrutiny intensifies, and reporting expectations become heavier than in previous cycles. What once passed as “good enough” operations may now grapple with volume, condensed timelines, and complexity.
Against this backdrop, fund operations must evolve. This is because operational maturity is the primary test of process resilience, trust, and execution.
In this article, we explore fund operations trends in 2026 and what GPs should prioritize.
1. AI and Automation Move From Experimentation to Core Infrastructure
In 2026, automation in fund operations is driven by capacity constraints, not innovation agendas. Lean operation teams now support complex fund structures, frequent reporting sequences, and broader regulatory demands. This is achieved without a proportional increase in headcount.
This shift aligns with industry data.
A McKinsey survey shows that 88% of organizations are now using AI in one or more business functions, and 20% in more than five functions.
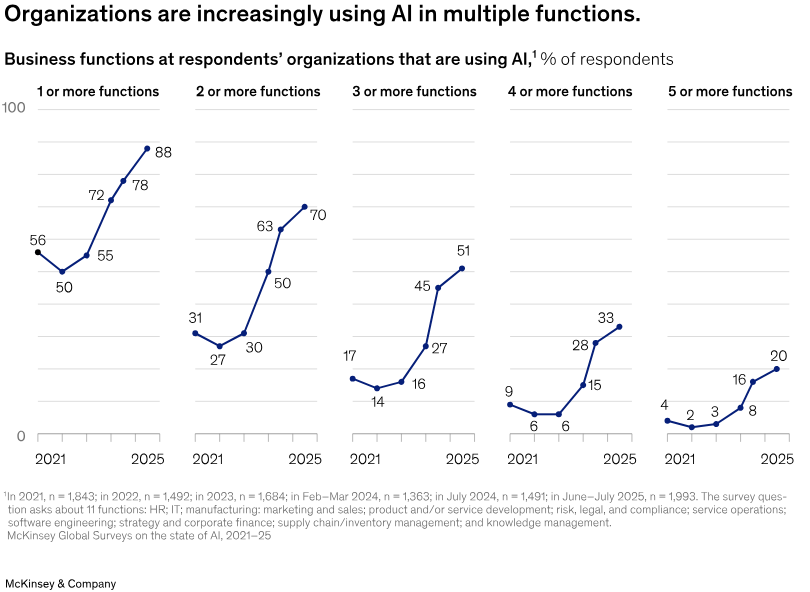
Still, nearly half of the larger networth companies have reached the scaling phase.
Deloitte also reiterates that the financial services industry has entered the digital marathon phase, changing how products and services are offered. The machines organize and interpret data to make accurate financial predictions based on this data.
Truth is, the highest value creation originates not from experimentation but from integrating automation into key, recurring workflows. These are exactly the areas under the most LP and regulatory scrutiny.
AI-driven tools are now being used in:
- ・Investor reporting and capital account statements
- ・Structured data retrieval from legal documents, financial statements, and side letters
- ・AML, KYC, and continuous compliance tracking
The operational benefit lies in predictability and control. Deloitte highlights that automation in financial services eliminates manual reconciliation, shortens close cycles, and minimizes error rates. These are the workflows most examined during operational due diligence and audits.
When LPs conduct their due diligence, they usually focus on whether:
- ・Key processes are repeatable across reporting cycles and fund vehicles
- ・Controls are integrated rather than dependent on individuals
- ・Operations remain adaptable as reporting volume and complexity grow
Automation has also raised governance expectations. A PWC survey shows that governance, oversight, and auditability are now core to technology risk awareness.
LPs and regulators are increasingly looking for:
- ・Accountability and clear model ownership
- ・Established exception handling and escalation paths
- ・Holistic auditability of automated workflows and outputs
Contextually, automation should be explained, tracked, or controlled. This way, it reduces the risk of new operational risks.
2. Data Standardization and Unified Reporting Become Non-Negotiable
According to EY, approximately US$24.4 trillion of capital is invested in the private market, and this value continues to grow.
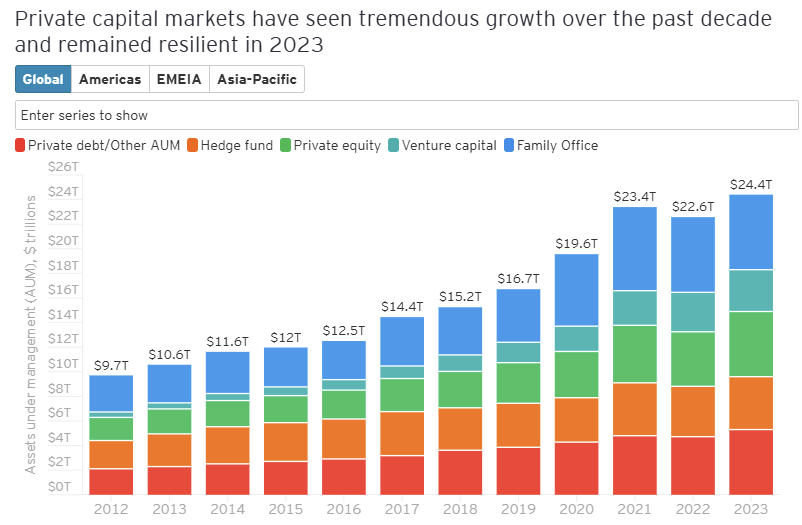
As the breadth of vehicles, strategies, and jurisdictions multiply, it also amplifies the operational strain. At this scale, fragmented data environments shift from being an efficiency issue to a structural constraint.
Disjointed accounting systems, erratic portfolio data, and spreadsheet-driven reporting make it more difficult for teams to deliver prompt, precise output across funds and investor groups.
In response, 2026 is seeking a clearer operational drift toward centralized data models. They augment investors, portfolio, and compliance reporting from a shared foundation.
As such, priorities now include:
- ・A single source of truth for NAV, exposure data, and performance
- ・Regularized KPIs used consistently across approaches, funds, and jurisdictions
- ・Explicit audit trails and information lineage from source systems through to investor reporting
LPs also consider a unified and reliable reporting as a key due diligence component. Data quality then directly influences GP’s ability to confidently:
- ・Address LPs’ due diligence
- ・Support fundraising
- ・Manage portfolio-level decision-making
This simply distinguishes operationally mature firms that prioritize consistency at the data source.
3. Fee Complexity, Liquidity Events, and Secondary Readiness
As fund structures continue to broaden, operational complexity increases. Fee processes have become operational challenges for private funds in 2026.
Extensions, continuation vehicles, and NAV-based facilities also introduce allocation rules, overlapping fee bases, and parallel waterfalls. These must stay consistent across investor classes and vehicles.
The increasing scale of liquidity activity explains why this issue matters operationally. In 2024, secondary transaction volume hit $162 billion globally. 40% of LP sellers used the market to generate liquidity.
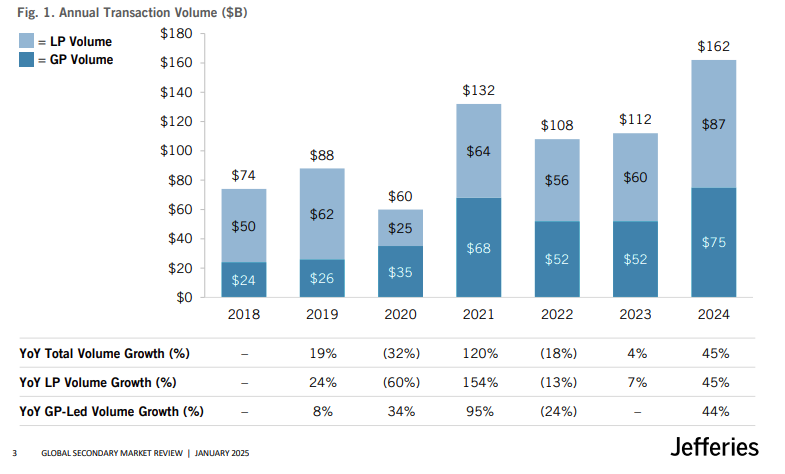
Liquidity events are regular, time-sensitive, and essential to the flow of capital through private markets. What makes them challenging is their timing and accuracy.
Transactions condense timeliness and reveal weaknesses in computational logic, financial integrity, and approval workflows. Errors that may stay concealed during periodic reporting tend to emerge quickly when capital is reallocated or when investors are reviewing transaction terms.
Here are the key areas where operational pressure typically concentrates:
- ・Complex fee and waterfall computations across parallel vehicles
- ・Allocation logic that must stay consistent and transparent across investor classes
- ・Swift production of precise, review-ready data for LPs, advisors, and counterparties
In these moments, even a small inconsistency can erode investors’ confidence. Compounded, it raises broader concerns about operational controls and scalability.
Therefore, liquidity events serve as operational stress tests. Only firms with automated calculations, structured review procedures, and clear allocation structures are better placed to perform smoothly.
Those without tend to reveal operational gaps at exactly the moment when precision matters most.
4. Cybersecurity, Third-Party Risk, and Operational Resilience
As fund operations get more centralized, operational risk accelerates. The concentration of portfolio data, sensitive investor information, and the reporting framework compounds the impact of failure. This may come from control gaps, vendor outages, or cyber incidents.
The risk and scale of cyber incidents are no longer theoretical. According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach approximated $4.4 million in 2025. Financial organizations recorded the second-highest average breach of $5.56 million.
For fund managers, cyber risk has a direct operational repercussion. It can disrupt reporting timelines, compromise data integrity, and force firms into reactive communications with investors and regulators.
Even breaches without immediate financial loss can delay transactions and spark comprehensive LP scrutiny.
Concurrently, dependency on third parties is on the rise. Fund managers, technology tools, data suppliers, and outsourced service collaborators now sit within primary operational workflows.
While this promotes scale, it also presents dependency risk. Control weaknesses at the vendor level swiftly become the GP’s responsibility.
As a result, operational securities are increasingly prioritized in these practical areas:
- ・Access controls and authorization that align with roles and responsibilities
- ・Data encryption and separation across funds, investors, and jurisdictions
- ・Continuous third-party risk analysis rather than isolated reviews
- ・Specified incident response and business progression plans
LPs value both prevention and resilience. During due diligence, they look for evidence that firms can still maintain operations through disruptions and restore reporting integrity without delay.
They also need assurance that the firm can communicate clearly and promptly during the incidents.
RAISE automates risk assessment and compliance to improve regulatory compliance.
What GPs Should Prioritize in 2026
In 2026, GP’s focus is more on stabilizing primary processes. It centers on those that directly affect investor confidence, reporting quality, and performance during high-pressure events.
Here are the immediate 2026 fund operations trends to prioritize:
- ・Shrinking manual reporting, reconciliation, and spreadsheet variations
- ・Harmonizing core datasets used across investor reporting, finance, and compliance
- ・Augmenting oversight of outsourced service providers and managers, with clearer accountability and escalation paths
These steps shrink key-person risk and limit the likelihood of errors during audits, liquidity events, and LP reviews.
Here are the midterm 2026 fund operations trends to prioritize
- ・Linking accounting, reporting, and compliance structures to minimize data handoffs
- ・Instituting repeatable workflows for complex fee, allocation computations, and waterfall
- ・Establishing scalable procedures for investor and regulatory reporting that do not depend on custom fixes
At this phase, the goal is resilience. Procedures and systems need to keep up as fund frameworks diversify, reporting frequency increases, and scrutiny rises.
Strategically, investment fund operations should be assessed through a narrow lens. Does it directly support:
- ・Fundraising
- ・Execution
- ・Investor trust
Platforms and procedures that do not minimize risk, boost transparency, or increase consistency tend to add complexity without conveying real operational benefit.
Operations as a Source of Competitive Advantage
In 2026, fund operations trends directly impact the firm’s ability to raise capital and perform reliably. As frameworks become more complex and LP scrutiny intensifies, weak procedures emerge faster and carry broader repercussions.
GPs who treat operations as critical infrastructure with minimal errors respond to due diligence confidently. They also address liquidity events without disrupting performance. For LPs, operational discipline is a signal of long-term reliability.
RAISE helps strengthen these foundations across data, execution, and reporting. For firms reexamining readiness for the next phase of growth, 2026 fund operations trends make operational discipline non-negotiable.
Request a demo to see how RAISE supports this across the fund cycle.